In this guide on How to Change SSH Port in Linux, you will learn how to change the SSH port on your Linux server to enhance security and reduce unauthorized access attempts. Changing the SSH port is a proven method to protect your system and optimize network traffic.
Step 1: Open the SSH Configuration File
Use a text editor like
nano to open the SSH configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
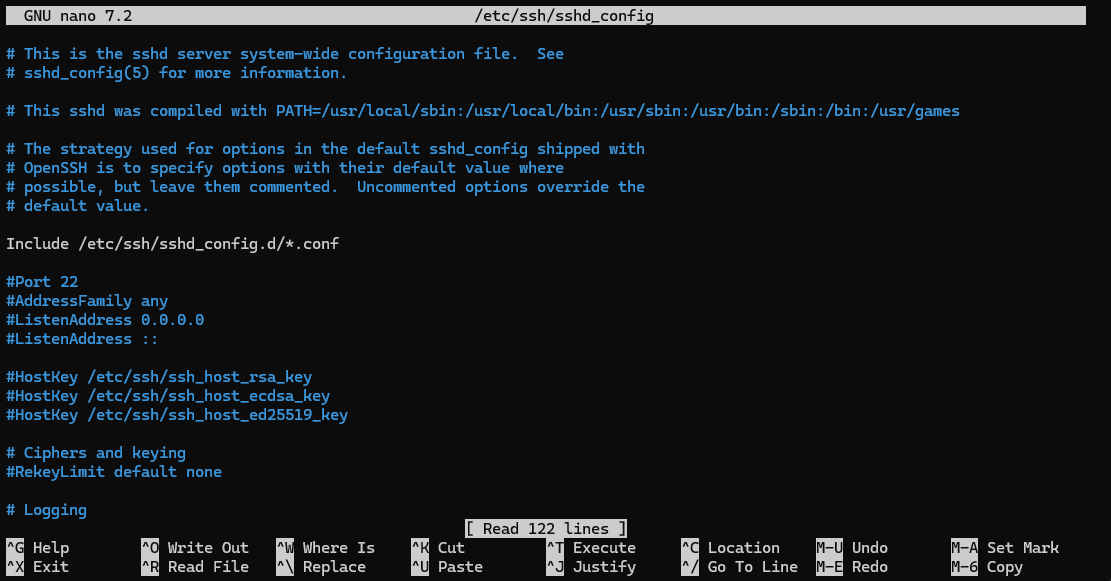
Step 2: Locate and Change the SSH Port Number
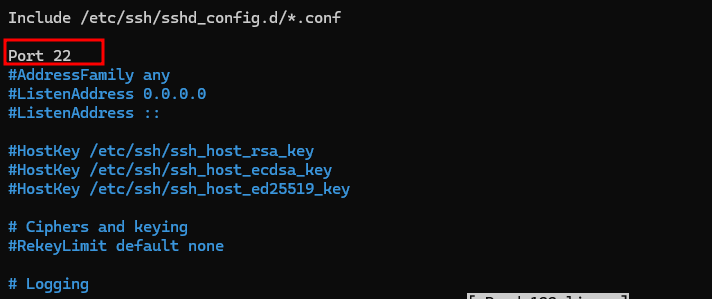
Find the line that specifies the SSH port (typically
port 22) and change it to your preferred port (e.g.,
2222):
port 22
Step 3: Save and Exit
After modifying the SSH configuration file, save and exit:
- Press Ctrl + X
- Press Y to confirm
- Press Enter
Step 4: Update Firewall Rules (Optional)
If your firewall is enabled, allow the new SSH port:
Step 5: Restart Your Server
Reboot your system to ensure the new settings take effect:
sudo reboot
Step 6: Connect Using the New SSH Port
After your server restarts, connect using the new SSH port. For example:
ssh user@your_server_ip -p [port_number]

Replace
[port_number] with your new port and
user@your_server_ip with your SSH username and server IP.
Ready to deploy your changes?
Deploy Now and
Learn How to Connect with IPv6 for enhanced security and connectivity.


