Layer 3 firewall is included with all servers offered by Evoxt. This will act as a defense line before inbound traffic reaches your servers. Layer 3 firewall performs slightly differently than a host-based firewall (the firewall in your server). Please spend some time understanding them.
Enabling the Firewall
Go to your VM control panel to manage the layer 3 firewall.
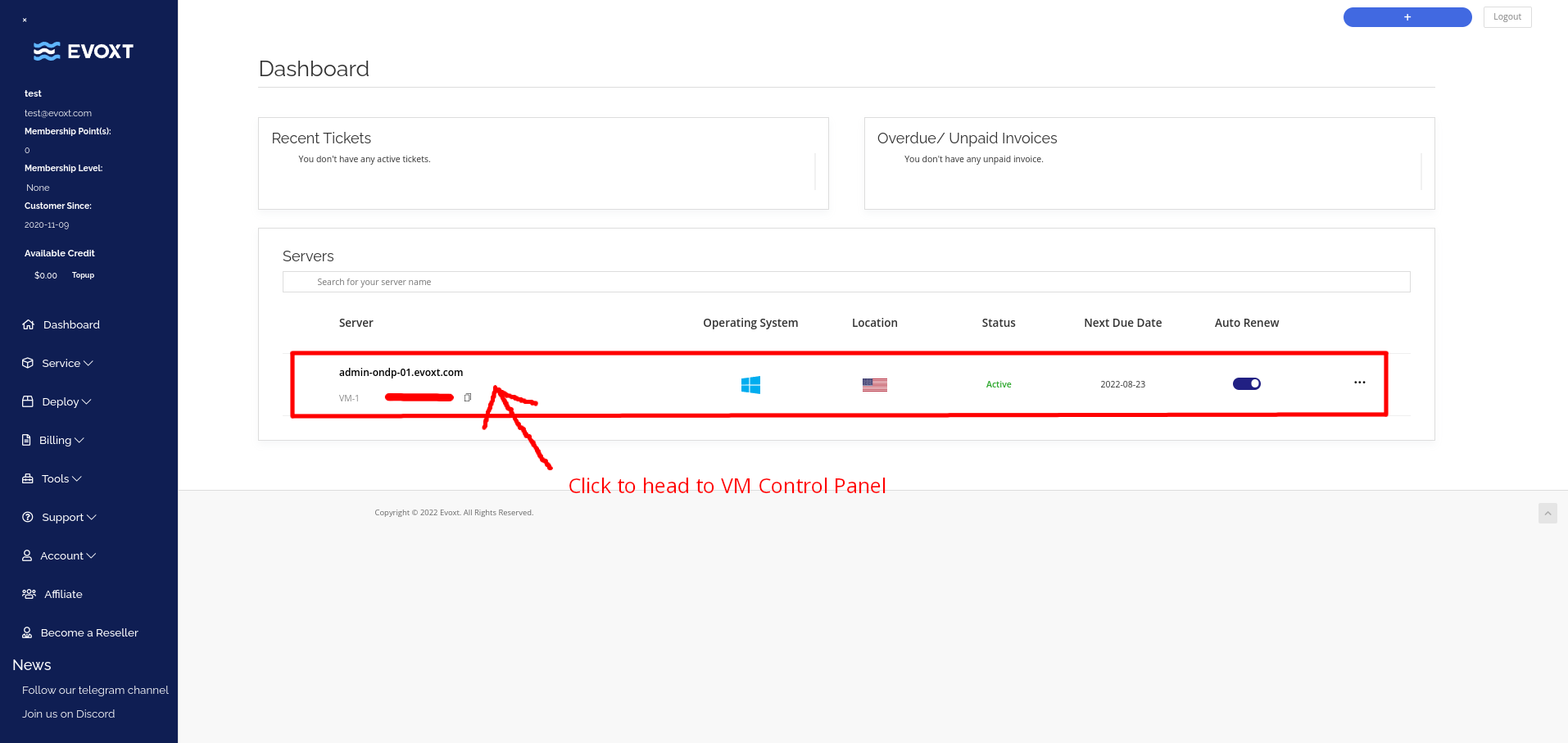
Then click on the Firewall on the top bar, as shown in the image below.
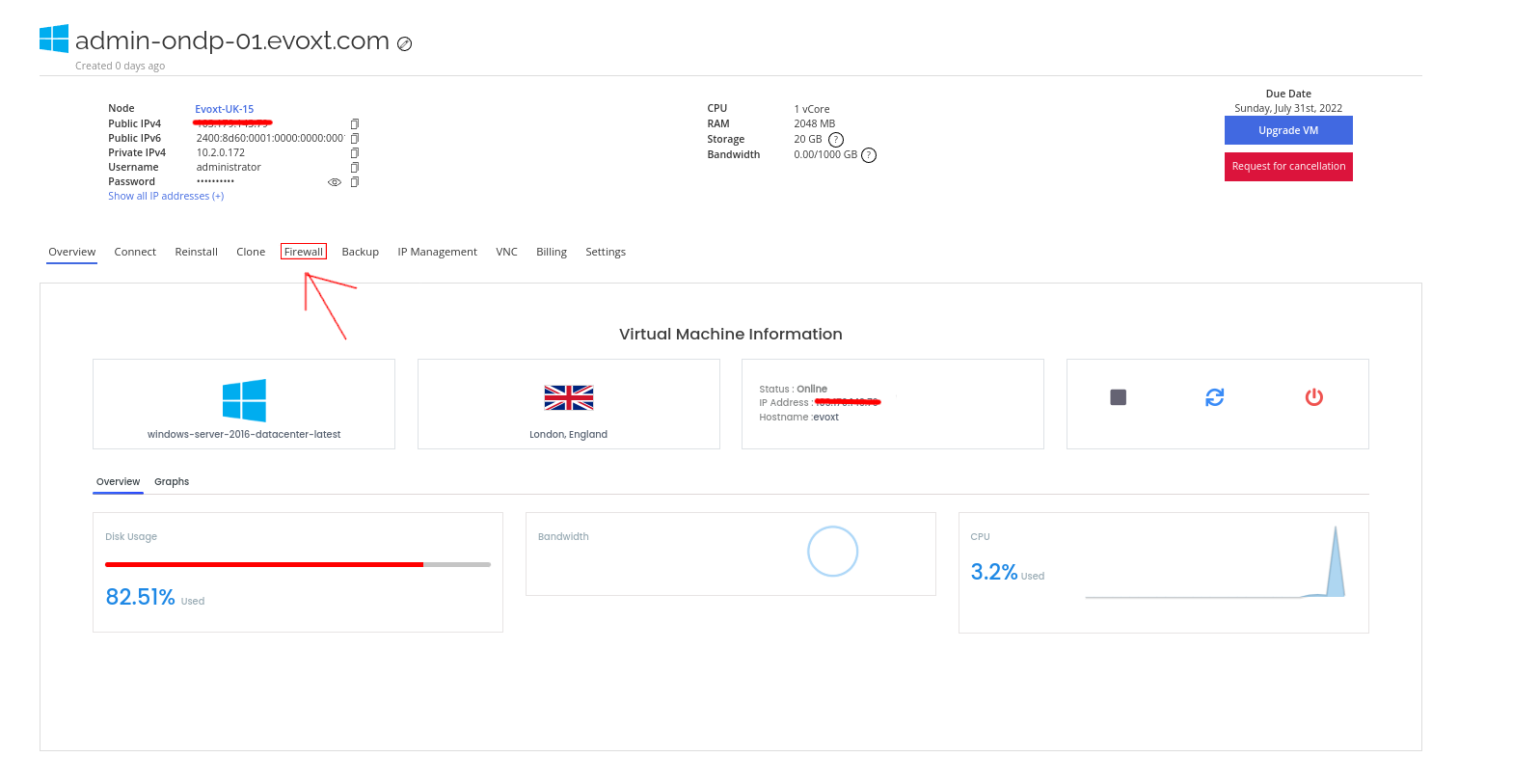
Introduction to the Firewall
Evoxt's Layer 3 Firewall is separated into 2 groups, IPv4 firewall, and IPv6 Firewall.
IPv4 Firewall manages all IPv4 inbound traffic, while the IPv6 firewall manages all IPv6 inbound traffic. Evoxt's Layer 3 Firewall
defaults to blocking all protocol and ports when enabled. All rules added are to allow the ports or protocol through the firewall.
To get started with managing the firewall and firewall rules, click on
Enable Firewall on the Firewall tab.
By default, there will be 5 firewall rules automatically added. This will be:
- TCP 32768 – 65535 (This rule handles the connection with private port, is a temporary communication hub used for Internet Protocol (IP) communications)
- UDP 32768 – 65535 (This rule handles the connection with private port, is a temporary communication hub used for Internet Protocol (IP) communications)
- TCP 0 – 65535 with the IP range 10.0.0.0/8 (This rule allow all inbound TCP traffic from servers that are located in the private network, all server that exists in the same region hosted at Evoxt)
- UDP 0 – 65535 with the IP range 10.0.0.0/8 (This rule allow all inbound UDP traffic from servers that are located in the private network, all server that exists in the same region hosted at Evoxt)
- ICMP with the IP range 10.0.0.0/8 (This rule allow all inbound ICMP protocol or ping from servers that are located in the private network, all server that exists in the same region hosted at Evoxt)
We strongly recommend deleting the list's 2nd, 3rd, and 4th rules if private networking is unnecessary. This ensures that the server is unreachable through Evoxt's private network to protect your server from any potential malicious server in the same network.
Suppose private networking is needed and the exact set of IP addresses that the server is communicating with is known. In that case, we recommend deleting the default rules and re-adding a more specific rule.
For example, two servers are under the same region in the same network. Their IP addresses are
10.0.1.1 and
10.0.1.2, server 1 and server 2 respectively.
On server 1, only allow the second server with the IP address
10.0.1.2/32 through the firewall.
On server 2, only allow the first server with the IP address
10.0.1.1/32 through the firewall.
With this configured, only these 2 servers can communicate, blocking any potential malicious connection attempts from servers in the same network.
Note: Do not forget about the IP address mask. In this case, this will be /32 for a single IP address.
Understanding the options
After enabling the layer 3 firewall, you will be greeted with this easy-to-use firewall panel.
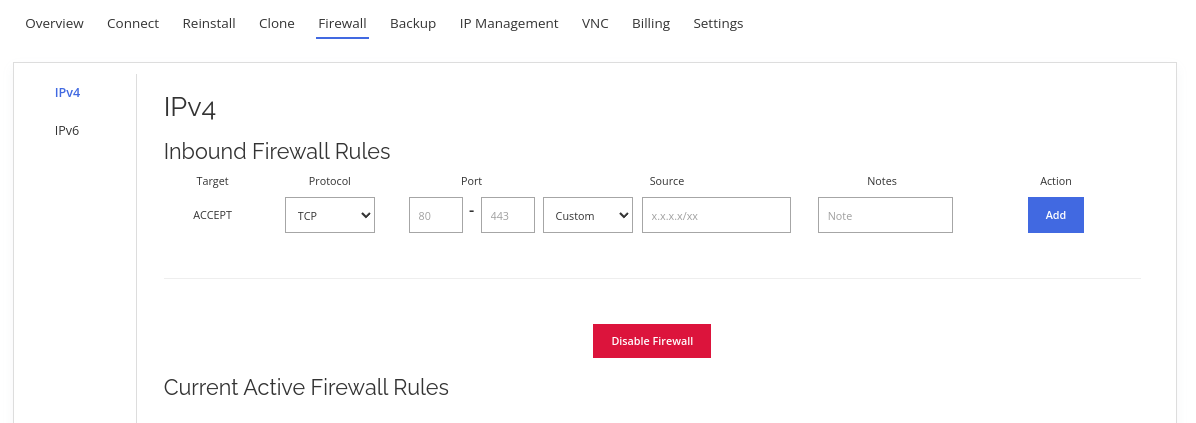
Below states the meaning for each of the fields and buttons:
- Protocol
Protocol to allow through the firewall. Most of the protocols that will be used are TCP and UDP.
- Ports
Ports to allow through the firewall. If only need to allow a single port is required, leave the second box empty. If this is a range, key in the starting port range in the first box and the ending port range in the second box.
- Source
The IP address that sends information to the server or the inbound IP address. Evoxt's Layer 3 Firewall only handles inbound traffic; the source will be the incoming IP address.
- Notes
Notes or Label for rules. Only alphabets, numbers, and spaces are allowed in this field.
- Add
Click on this button to add a firewall rule.
- Disable Firewall
Clear all firewall rules and disable the firewall.
- Delete
Delete the specific firewall rule.
Common Firewall Rules Settings
Here are some screenshots of the most common firewall rules,
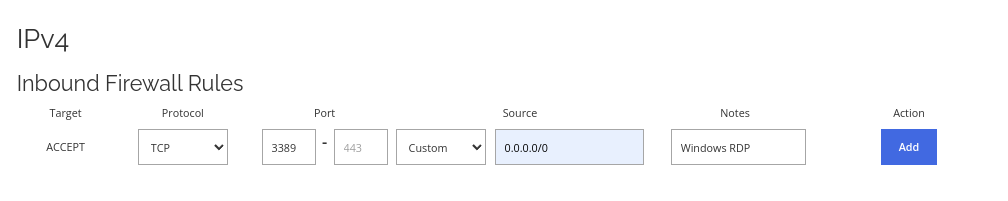 Allow RDP through the firewall.
Allow RDP through the firewall. If your server runs on Windows, you will likely need to add this rule to remote control your server. Follow this screenshot to enable RDP through layer 3 firewall.
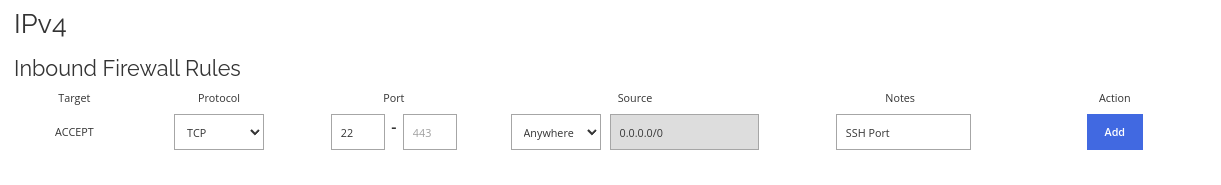 Allow SSH through the firewall.
Allow SSH through the firewall. If your server is running on Linux based OS, you most likely will need to add this rule to remote control your server.
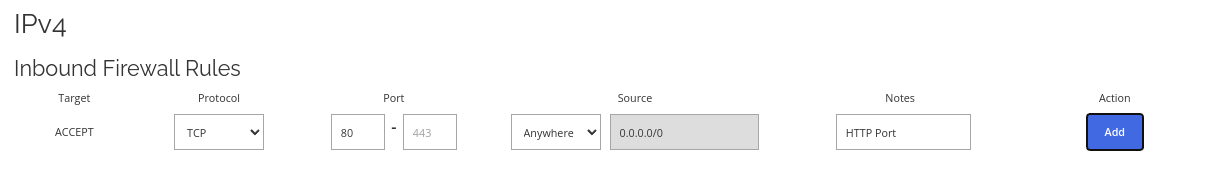 Allow HTTP port through the firewall.
Allow HTTP port through the firewall. If you are running a web server or hosting a website, this is the default non-SSL port. You will most likely need this to set up a web server or website along with an HTTPS port rule.
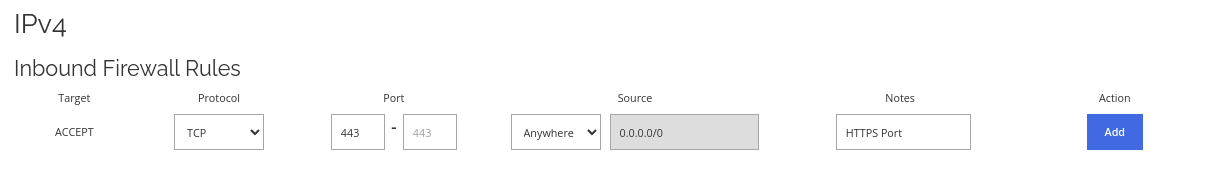 Allow HTTPS port through the firewall.
Allow HTTPS port through the firewall. This is the default SSL port for running an HTTPS web server. You will likely need this to set up an HTTPS web server or website.
 Allow connections to the database.
Allow connections to the database. This is the database default connection port.
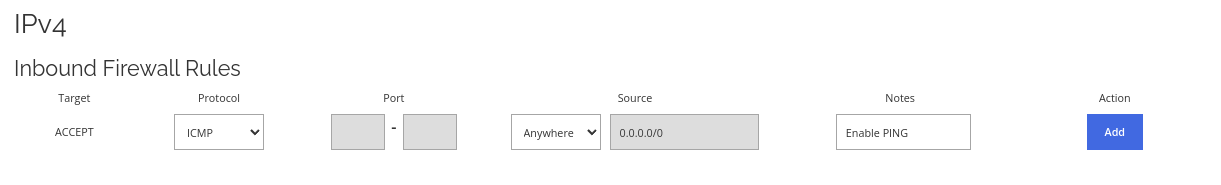 Allow incoming ping requests to your server.
Allow incoming ping requests to your server. Enable this if you want your ping request to reach your server. This is very useful for doing uptime monitoring.
However, this can potentially be dangerous. Hackers can use this protocol to check if your server is online by pinging your server's IP address and attempting to gain unauthorized access to your server. Besides that, by enabling ICMP protocol, your server will also be susceptible to some types of DDoS attacks.
Hence, if you want your server to be pingable, we strongly suggest setting a stricter IP source rule to protect your server.
IPv6 Layer 3 Firewall
IPv6's layer 3 firewall acts the same as IPv4, but it regulates inbound connection for IPv6 protocol. The control for the IPv6 firewall is the same as the IPv4 firewall, but the initial rules that will be added when the firewall is first enabled will be slightly different.
When IPv6 Firewall is enabled, 3 firewall rules are automatically added. This will be:
- TCP 32768 – 65535 (Which handles the connection with private port, is a temporary communication hub used for Internet Protocol (IP) communications)
- UDP 32768 – 65535 (Which handles the connection with private port, is a temporary communication hub used for Internet Protocol (IP) communications)
- ICMPv6 on the IPv6 block of the server's IPv6 address is in. This is needed to ensure IPv6 is functioning properly. IPv6 requires ICMP to function properly. Hence this specific rule is added. We strongly recommend not disabling this rule.
Unlike the IPv4 firewall, there is no private IPv6 network with Evoxt, so no Private network rules are required.
Difference between Evoxt's Layer 3 Firewall and Host-based Firewall (Windows/ Linux Firewall)
-
On a host-based firewall, firewall software or similar programs might need to be installed on the server for the firewall to function. In contrast, Evoxt's Layer 3 Firewall does not require any software installed.
-
Evoxt's Layer 3 Firewall operates on the network layer, which means malicious traffic can be blocked before it reaches the server. In contrast, a host-based firewall will start processing the packet when the packet reaches the server, leading to potential security flaws. Besides that, because a layer 3 firewall does not exist in the system, a lot of traffic and processing power can be saved during a DDoS attack when the malicious packets are dropped before reaching the server.
-
Layer 3 firewall will provide a stronger defense than a host-based firewall because this operates on the network layer, separated from the server, which is not susceptible to tampering or backdoors.
-
Evoxt's Layer 3 Firewall is easy to understand and set up. In Linux operating system, setting up a firewall usually requires some comfort in CLI skills, while Evoxt's Layer 3 Firewall only takes a few clicks to get a firewall set up.
-
Layer 3 firewall is not "intelligent" compared to a host-based firewall because a layer 3 firewall operates on the network layer and will not understand information on the application layer. This means that firewall blocking, such as based on the application type or only allowing established connections, cannot be set. With layer 3 Firewall, a rule can only be set by using a protocol, port, or IP address only.
As you can see, there are upsides and downsides with both firewalls. To fully protect your server, we strongly recommend setting up both firewalls for maximum protection.
Common DDoS attacks that can be mitigated with Evoxt's Layer 3 Firewall
- UDP Flood – Only allow the UDP ports in use through the Firewall. If access is not public, consider allowing only a specific IP address through the UDP port that is in use.
- ICMP (Ping) Flood – Block ICMP Protocol to block all ping requests. This can be done by enabling the firewall, which defaults to blocking all protocol and ports.
- Ping of Death – Block ICMP Protocol to block all ping requests. This can be done by enabling the firewall, which defaults to blocking all protocol and ports.










