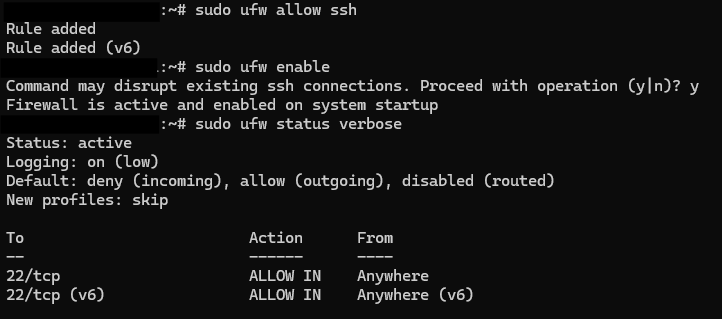
sudo apt update sudo apt install ufw -y # ensure SSH allowed first: sudo ufw allow ssh # enable firewall sudo ufw enable
sudo ufw allow 12345/tcpAllow UDP port 12345:
sudo ufw allow 12345/udpAllow a port from a specific IP only (example: allow 12345 from 203.0.113.5):
sudo ufw allow from 203.0.113.5 to any port 12345 proto tcp
sudo ufw status numbered sudo ufw status verbose
# see rule numbers sudo ufw status numbered # delete rule by number (example deletes rule #3) sudo ufw delete 3Or delete by exact rule text:
sudo ufw delete allow 12345/tcpTo explicitly block (deny) a port:
sudo ufw deny 12345/tcp
ufw enable persists across reboots.sudo ufw logging on to view blocked attempts in /var/log/ufw.log.sudo dnf install firewalld -y sudo systemctl enable --now firewalld
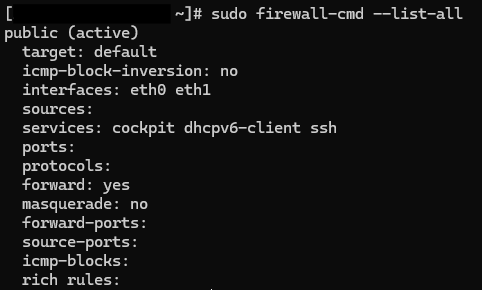
public). You can add ports/services to the active zone or to a specific zone.
# show default zone sudo firewall-cmd --get-default-zone # list active zones & settings sudo firewall-cmd --list-all
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=12345/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --reloadRuntime only (temporarily persists until next reload/reboot):
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=12345/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https sudo firewall-cmd --reload
sudo firewall-cmd --list-ports sudo firewall-cmd --list-services sudo firewall-cmd --list-all
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-port=12345/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --reloadRemove a runtime-only port:
sudo firewall-cmd --remove-port=12345/tcpRemove a service (e.g., HTTPS):
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-service=https sudo firewall-cmd --reload
--permanent to persist across reboots; otherwise rules are runtime-only.nc (netcat) to test TCP ports:
# test port 12345 nc -zv YOUR-SERVER-IP 12345
Result meanings:
Connection succeeded — port open & allowedConnection refused — service not listening on that portConnection timed out — port likely filtered/blocked by firewall or network-level filtersudo ufw logging on sudo tail -f /var/log/ufw.logFor firewalld, enable denied logging and check the journal:
sudo firewall-cmd --set-log-denied=all sudo journalctl -f -u firewalld
sudo apt install ufw -y sudo ufw allow ssh sudo ufw enable # allow custom TCP/UDP port sudo ufw allow 12345/tcp sudo ufw allow 12345/udp # allow from specific IP sudo ufw allow from 203.0.113.5 to any port 12345 proto tcp # remove by rule number sudo ufw status numbered sudo ufw delete [number] # delete by rule sudo ufw delete allow 12345/tcp # explicitly deny sudo ufw deny 12345/tcp # status sudo ufw status verbose
sudo dnf install firewalld -y sudo systemctl enable --now firewalld # allow custom TCP port permanently sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=12345/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --reload # allow runtime-only sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=12345/tcp # remove permanent port sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-port=12345/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --reload # allow a service (HTTPS) sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https sudo firewall-cmd --reload # list rules sudo firewall-cmd --list-ports sudo firewall-cmd --list-services