This guide explains how to set up Linux startup scripts using systemd. It shows how to automatically run commands when your server starts, optionally run scripts during shutdown, and manage service behavior. This method works on Linux systems such as Ubuntu, Debian, AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux, and RHEL.
Step 1: Create the Startup Script
Systemd runs scripts at boot using service units. First, create a script that performs the startup actions you want.
sudo nano /usr/local/bin/startup.sh
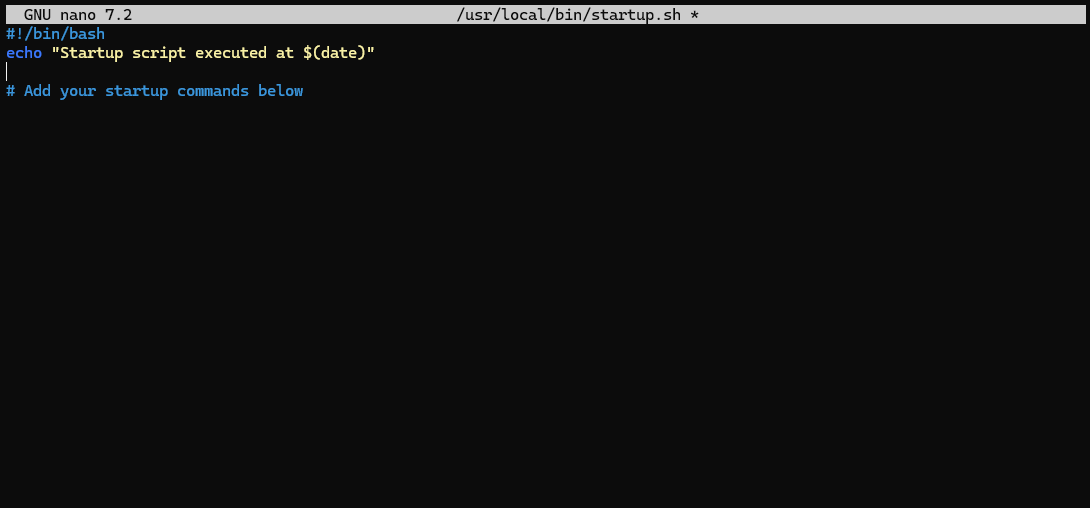
Add the following lines:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Startup script executed at $(date)"
# Add your startup commands below
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/startup.sh
Tips:
- Always use the full path to your script (e.g.
/usr/local/bin/startup.sh).
- Store your script in
/usr/local/bin for easy access.
- Make sure the script is executable using
chmod +x.
Step 2: Create a systemd Service
Now, create a service file that runs the script on boot.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/startup.service
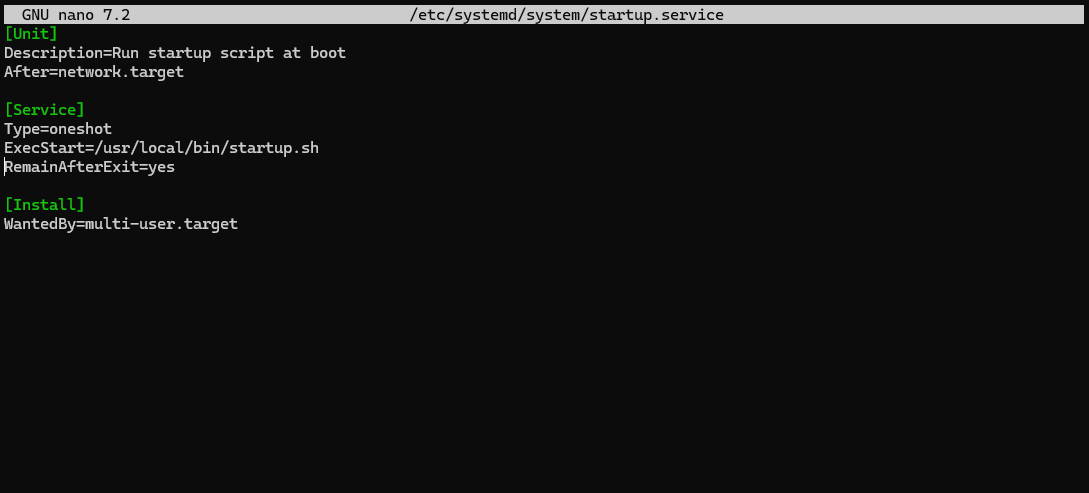
Add the following content:
[Unit]
Description=Run startup script at boot
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/startup.sh
RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable --now startup.service
Systemd will now execute your script automatically when the VPS boots.
Step 3: Add a Shutdown Script (Optional)
Systemd can also run a command when the system shuts down or when a service stops. Repeat steps 1 and 2, but use
ExecStop instead of
ExecStartto your service configuration.
[Service]
ExecStop=/usr/local/bin/stop.sh
This is useful for saving data or cleaning up temporary files during shutdown.
Step 4: Monitor and Troubleshoot
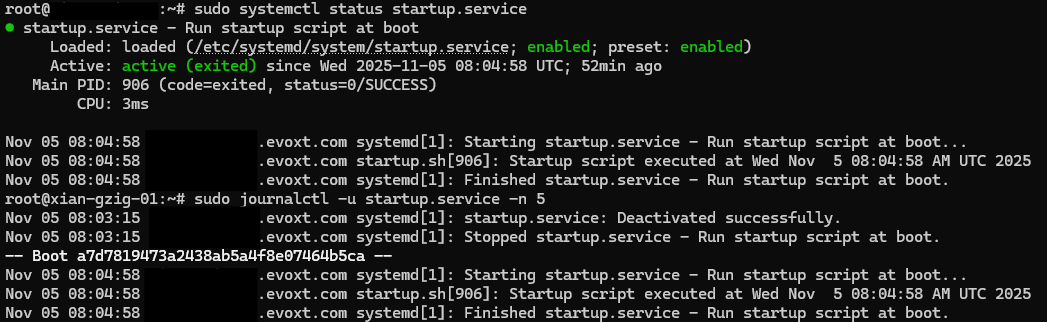
You can monitor service logs and verify if the script ran successfully:
# Check status
sudo systemctl status startup.service
# View logs
sudo journalctl -u startup.service -n 10
Use sudo systemd-analyze verify /etc/systemd/system/startup.service to check for syntax issues in your service file.
Conclusion
Using systemd for startup scripts is the most reliable and modern way to automate tasks on Linux. It ensures your scripts run at boot, can restart automatically, and provides centralized logging for easy troubleshooting. Optional shutdown hooks make it easy to clean up resources safely.
By following these steps, you can confidently manage startup, background, and shutdown behavior on your Evoxt Linux VPS with full control and stability.
For more Evoxt VPS guides, visit
Evoxt Tutorials. If you need assistance,
open a support ticket.



