Securing your Linux server with SSH keys enhances security by enabling passwordless authentication while preventing brute-force attacks. This step-by-step guide will help you configure SSH keys efficiently and safely.
Step 1: Generate an SSH Key Pair
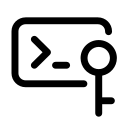
To create an SSH key pair, open a terminal on your
local machine and run:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
-t rsa specifies the RSA encryption type, ensuring strong security.-b 4096 generates a 4096-bit key, providing enhanced protection.
During this process, you'll be prompted to:
- Choose a file location (Press Enter to use the default
~/.ssh/id_rsa).
- Set a passphrase (Optional but recommended for added security).
Step 2: Log in to Your Linux Server
Before copying the SSH key, log in to your server using your existing credentials:
ssh user@your-server-ip
Replace
user with your actual
Linux username and
your-server-ip with the
server’s IP address.
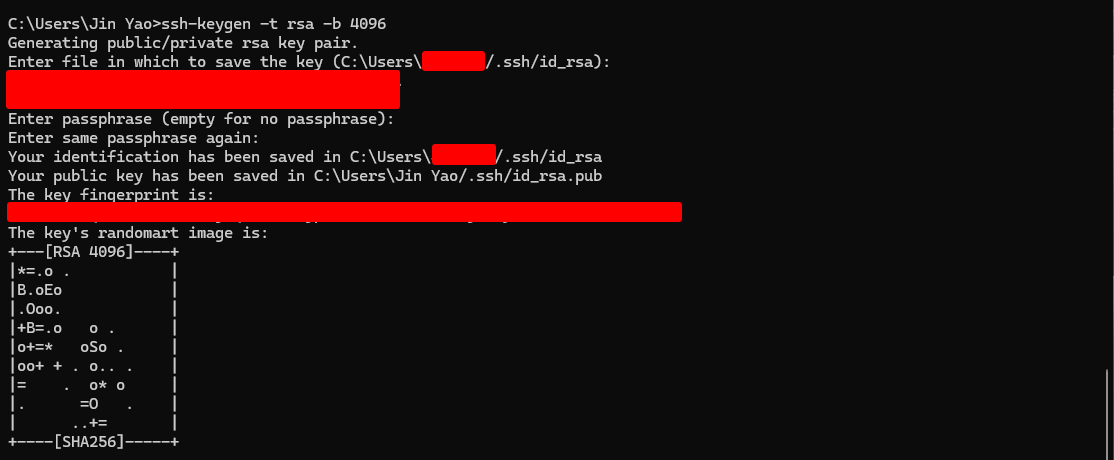
Step 3: Copy the Public Key to Your Linux Server
Once the key is generated, copy the
public key (
id_rsa.pub) from your local machine to the
server’s ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file.
Run the following command
on your Linux server:
echo your-public-key >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Example SSH Key Format
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEA7nVdS7h9QhMhAaaOBFZtclWZtBQKdb...
zBQKdb6yGGHt5h7IY+bprOSoK+cBoZd+aQ8pfqL9iT+xxuUbfSTGVJw== user@hostname
Step 4: Set Correct Permissions
To
ensure security, adjust the SSH directory and file permissions:
chmod 700 ~/.ssh
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
These commands
restrict access, allowing only the user to modify or read SSH keys.
Step 5: Test SSH Key Authentication
Now, test your SSH key login:
ssh user@your-server-ip
If configured correctly, you will log in
without needing a password.
Step 6 (Optional): Disable Password Authentication for Extra Security
To prevent password-based logins, disable them in the SSH configuration file.
1) Open the SSH configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
2) Find and modify the following line:
Change:
PasswordAuthentication yes
To:
PasswordAuthentication no
Save and exit by pressing: Ctrl + X → Y → Enter.
Now, only
SSH key authentication will be allowed for remote logins. Changes to PasswordAuthentication should take effect immediately without needing to restart SSH. After editing, run
sudo sshd -T | grep passwordauthentication to confirm the setting. If the output still shows "yes," check
/etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/ for any additional configuration files that might be overriding your settings.
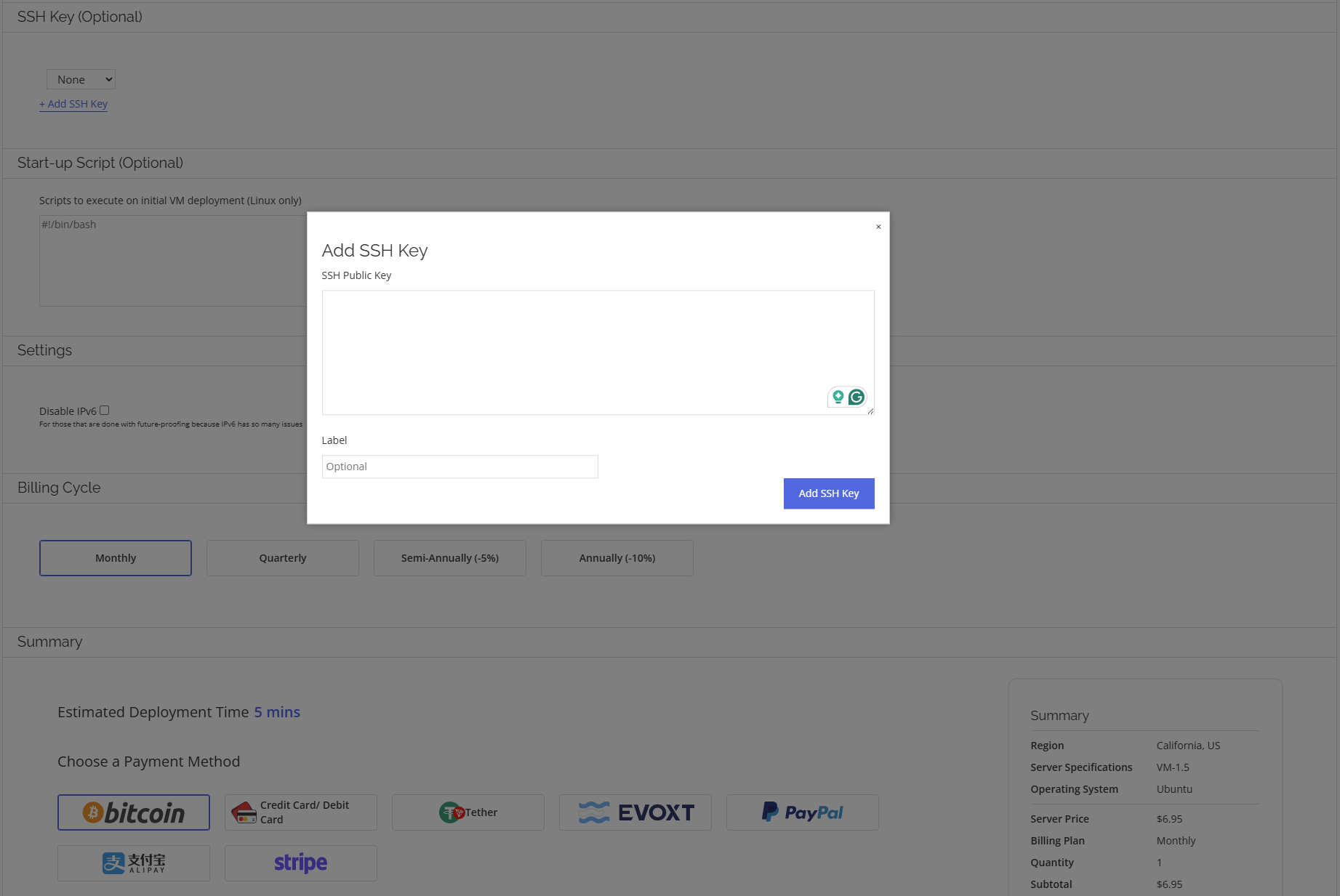
Optional Step: Add Your SSH Key During Server Deployment
When deploying your server through Evoxt, you have the option to add your SSH public key during the setup process. This enables secure, passwordless authentication right out of the box.
Quick Commands Recap
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
echo your-public-key >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
chmod 700 ~/.ssh
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Why Use SSH Keys for Secure Authentication?
- ✅ Prevents brute-force attacks by eliminating password-based logins.
- ✅ Enables passwordless access, improving efficiency and automation.
- ✅ Enhances security through strong cryptographic encryption.
By following these steps, you can
secure your Linux server with SSH key authentication, reducing vulnerabilities and ensuring
safer remote access.
For additional guidance, check out:
How to Change Your Linux Password or contact
Evoxt Support.